IoC(Inversion of Control, 控制反转), 是指应用本身不负责依赖对象的创建及维护,
而 依赖对象 的创建及维护是由外部容器负责的.
核心
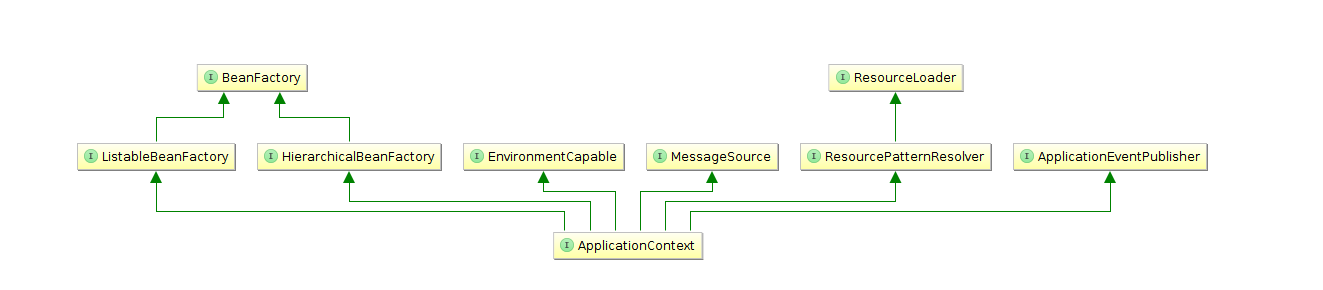
要了解 IOC 容器内部, 首先要了解 BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext.
BeanFactory 是访问 spring bean 容器的根接口, ApplicationContext 则作为高级容器, 为应用提供配置/事件发布等功能.
如下图所示:
BeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory
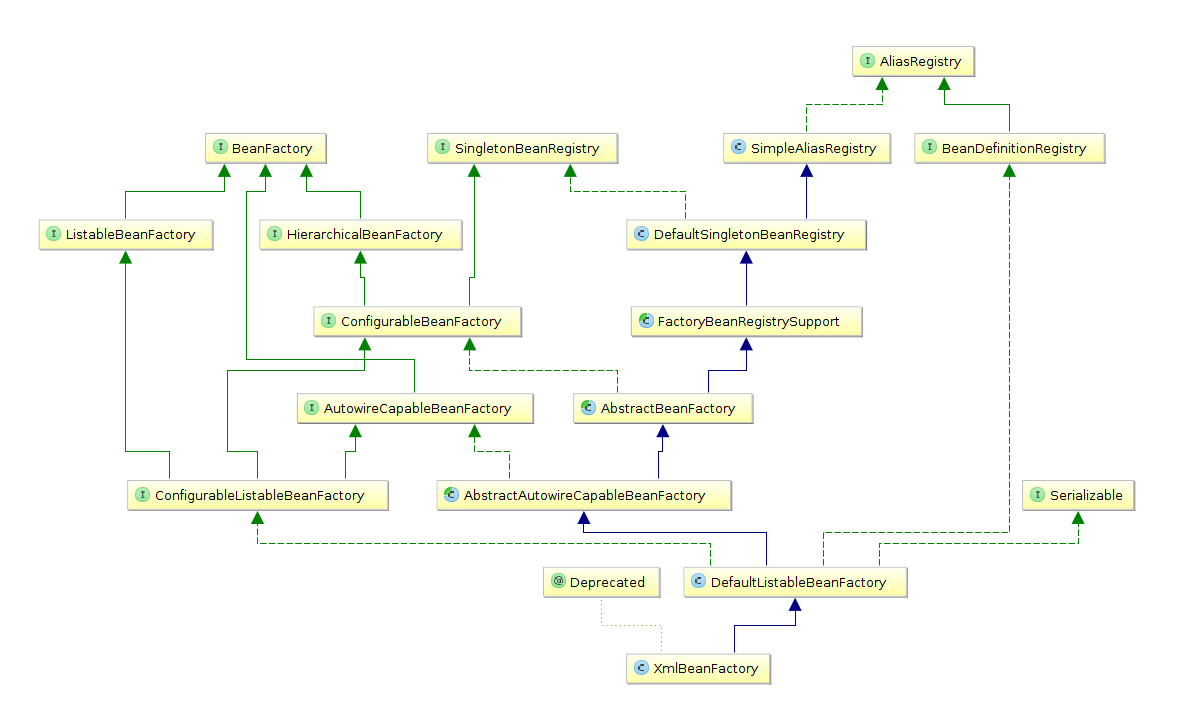
说起 BeanFactory, 这里以它的实现之一 XmlBeanFactory 为例:
设计图:
首先 XmlBeanFactory 继承了 DefaultListableBeanFactory,ListableBeanFactory 和 BeanDefinitionRegistry 的默认实现, 是功能完全的 bean factory, 后面会经常提到:
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { |
编程的方式使用 IoC
BeanFactory 是低级容器, 作为基本容器, 可以直接编程使用:
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml"); |
ApplicationContext
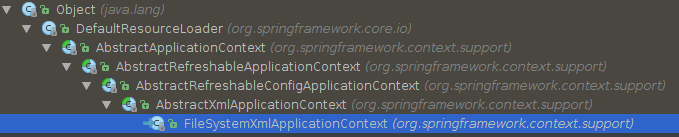
以 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 为例:
因为继承了 AbstractApplicationContext , AbstractApplicationContext 继承 DefaultResourceLoader, DefaultResourceLoader 是默认的Resource资源加载器, 实现 ResourceLoader 接口, 因此可以获得 Resource 定义的 BeanDefinition 的能力.
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 继承:
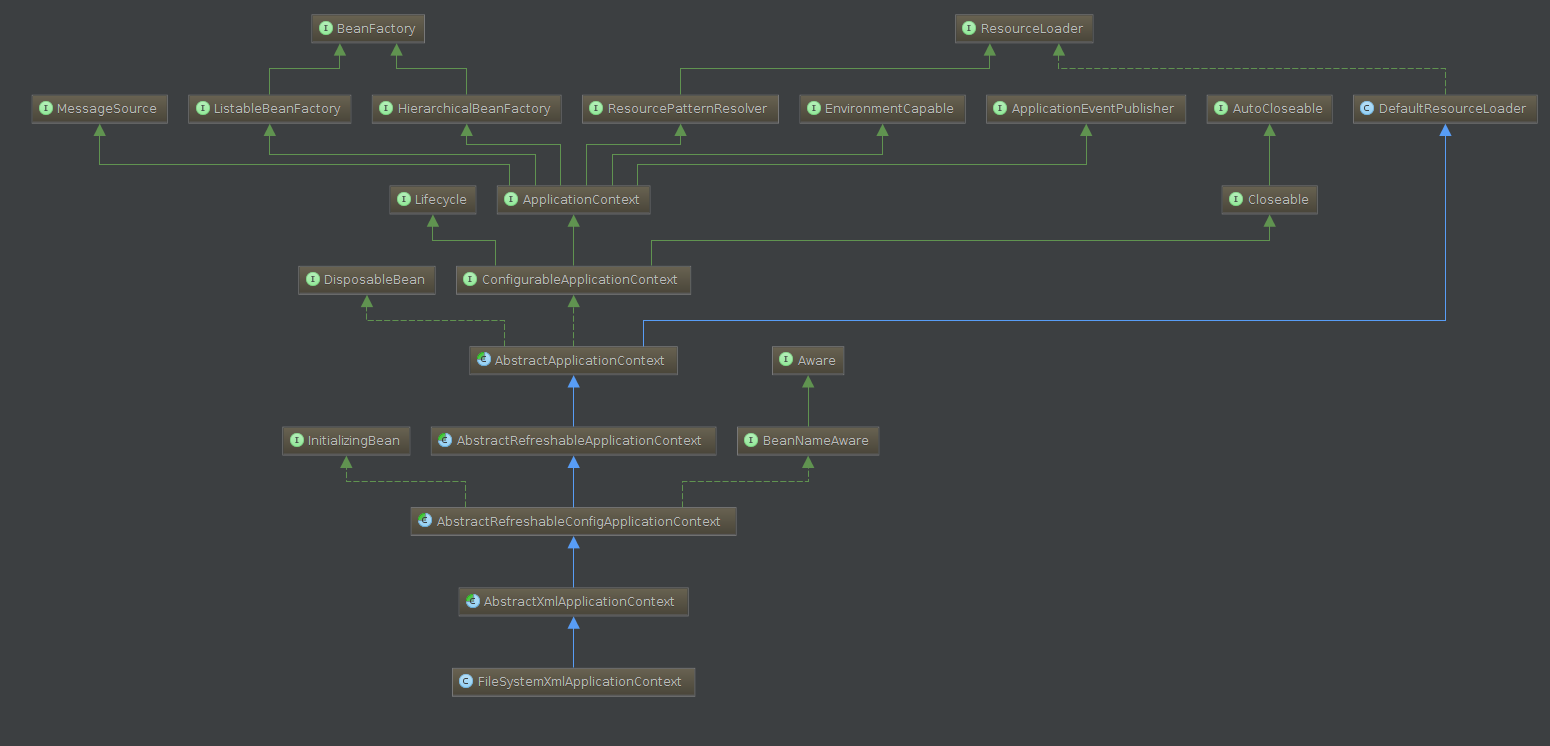
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 更详细的类和接口关系:
它的核心构造器 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) 中, refresh() 就是进行容器初始化的过程, 后面会提到里边的具体实现.
public class FileSystemXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext { |
接下来, 就继续以 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 为例, 介绍容器初始化过程 :
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext |
Resource 加载
用过spring的童鞋都知道, 首先我们会定义一些bean, 容器初始化当然也要首先读取这些bean的定义, 这些定义 spring 中对应的是 BeanDefinition 接口. spring 容器将会读取 Resource 配置加载 bean,因此首先要找到 Resource。
在上面 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 的构造器中, 作为入口,首先 super() 执行父类的构造器,获取 ResourcePatternResolver :
public AbstractApplicationContext() { |
ResourcePatternResolver 可以将 configLocations 转换成相应的 Resources:
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader { |
结合前面的 hierarchy 图来看, 因为 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 实现了 ResourceLoader 和 ResourcePatternResolver, 因此有获取 Resource 的能力,这在后面加载 bean 定义的时候非常有用 :
ResourceLoader 定义:
public interface ResourceLoader { |
继续看 hierarchy 图, 看 ResourceLoader 的第一个实现 DefaultResourceLoader 的 getResource(String location) 内容:
|
org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 作为子类, 覆盖了 getResourceByPath(String path), 从而使 FileSystemResource 替代 ClassPathContextResource :
|
初始化
能够获取到 Resource 之后, 我们就可以据此载入 BeanDefinition, 开始IoC容器的初始化, 继续看前面 AbstractApplicationContext 构造器中的refresh(), 里边的一连串方法就是初始化的过程 :
|
在上面的 obtainFreshBeanFactory() 中:
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { |
其中, refreshBeanFactory()需要关注一下, 看一下实现 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 的 refreshBeanFactory() :
|
createBeanFactory() 就是创建 DefaultListableBeanFactory 的地方 (这个类的作用和重要性在前面介绍过了) .
载入 BeanDefinitions
接着上面的 loadBeanDefinitions() 就是加载 BeanDefinition , 它是一个抽象方法, 我们首先看 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 的实现:
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory)
|
上面的 loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) 中使用 XmlBeanDefinitionReader, 和前面我们介绍的编程式使用 IoC 是一样的.
值得注意的是, beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this), 从 hierarchy 图中可知, AbstractXmlApplicationContext 继承了 DefaultResourceLoader, 所以 this 已经有获取 Resource 的能力.
由于上面的 Resource 是一个数组, 首先会调用 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions(Resource ...)
|
然后才是 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource):
|
其中, XmlBeanDefinitionReader.doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); 是重点, 它把 Resource 解析成 Document, 接着执行 registerBeanDefinitions() 的操作, 如下:
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) |
解析 BeanDefinition xml
接着上面的 XmlBeanDefinitionReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); ,这里使用 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 来解析并注册:
registerBeanDefinitions
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { |
继续, BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.registerBeanDefinitions() :
|
开始解析和注册:
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.doRegisterBeanDefinitions
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { |
首先看 createDelegate() , 创建了 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate, 这个 Delegate 将会完成 XML bean definitions 的解析.
protected BeanDefinitionParserDelegate createDelegate( |
继续看 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.parseBeanDefinitions:
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { |
bean 在xml中的配置, 如 property / ref / value / scope 等属性都会在这个 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 中解析 ( 在parse*()方法 ), 具体的xml解析过程太细节, 这里只关注主流程和关键的.
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { |
上面的 getReaderContext() 是 beanDefinitionReader, 还记得前面的 AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions() 否:
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory |
XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的构造器是 :
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { |
从前面的设计图亦可知道 DefaultListableBeanFactory 实现了 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry :
BeanDefinitionRegistry:
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistry extends AliasRegistry { |
注册 BeanDefinition
接着上面的 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()) 完成注册工作 :
public static void registerBeanDefinition( |
在 DefaultListableBeanFactory 中, 有一个 ConcurrentHashMap 来持有 BeanDefinition, 如下:
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */ |
主要看 registry.registerBeanDefinition() 的具体实现 -> org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition :
|
至此, 已经完成了初始化操作, 建立了 beanDefinitionMap 等内部映射. 下一博客将讨论 IOC 容器如何完成 bean 的依赖注入.